Hardness refers to the ability of a material to locally resist hard objects from being pressed into its surface. It is an important mechanical property and an indicator for comparing the softness and hardness of various materials. Hardness does not have a unified meaning. The physical meaning of hardness value varies with different test methods, and its various hardness units are also different.
There are many hardness testing methods, including the scratch method and the indentation method. The Rockwell hardness testing method discussed in this article belongs to the indentation method. The principle is: the hardness value of the material is expressed by measuring the indentation depth value.
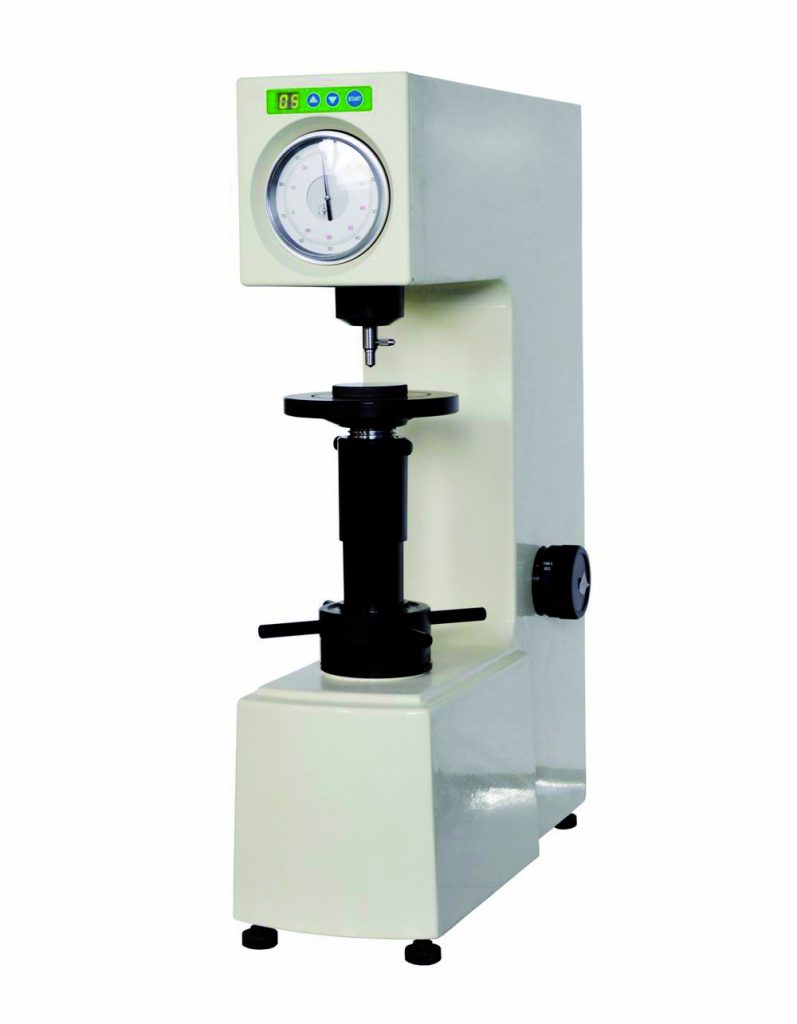

- Things to note
The Rockwell hardness test relies on the depth value of the indenter on the specimen. Every factor that affects the depth value will lead to errors in the readings, which are described below:
1).Test piece
In order to obtain an accurate value, the specimen must have a certain thickness to ensure that there is no small indentation on the lower surface of the specimen after testing. This limit thickness value changes with the hardness of the test material. Usually the limiting ratio of thickness to depth should exceed 8. If the thickness of one sample does not meet the requirements, two or more samples can be stacked until the thickness meets the standards.
In terms of size, it should also be noted that the center of the indentation is not less than 2 times the diameter measured from any edge of the specimen, and a distance of 4 times the diameter of the indentation must be maintained between two adjacent indentation lines.
The surface of the specimen must be kept clean and free from contamination, scratches, or human damage.
2).Measuring head
When testing, a suitable measuring head should be selected so that the test piece will not slide, roll or sag. If the test piece is not placed on a suitable measuring head, not only will the accuracy reading not be obtained, but the indenter will also slip and be damaged.
There are three types of measuring heads:
Flat Measuring Head: It has a flat surface and is used for testing heavy objects with a flat bottom.
Point measuring head: It has a small liftable surface and can be used for testing small parts, thin parts or objects whose bottom is not completely flat. Because the contact point between the test piece and the measuring head at the bottom of the indenter is very critical during testing.
V-type measuring head: small, it has a V-shaped groove, used for round specimens (diameter less than 3mm); large, used for large-diameter round specimens, such as round rod-shaped objects.
3).Load speed and load support time
The speed of measuring large loads is controlled by a vibration damping cylinder filled with shaft lubricant. Speed is affected by changes in oil viscosity, which are affected by seasonal changes and changes in operating room temperature. For the operator, it is necessary to determine the load speed and load control time according to the material to be tested.
4).Indenter
The indenter of the L-2020 hardness tester is a spherical indenter, not a diamond indenter.
When a hard ball is used, it is difficult to change its shape on a material softer than HRB. Unless the test is performed before the hardness of the steel body is unknown, it may be worn by the hard steel body specimen. Such testing will cause permanent deformation of the ball, which requires the ball to be repaired at all times, and the ball seat is also manufactured to be suitable for ball repair.
When replacing the ball, note that the indenter cap controls the proper position of the ball. The cap must leave at least 1/3 of the ball exposed below the pressure head. If the indenter cap is screwed onto the ball, use only finger pressure on the ball to make it easier to control. The end of the ball positioning screw must be purged clean. There should be no dust or debris at the contact point between the shoulder of the support and the bottom of the specimen.
Loosen the pressure head screw slightly and then tighten it again. The inside of the indenter screw is a double structure with a spring, which controls the vertical hammer of the indenter. - Error analysis
1).The reading is too high
First look at the pressure point of the indenter. The reading will be high due to the flattening of the ball. Friction during operation, the presence of dust or debris will also cause the reading to be high.
2).The reading is low
If the instrument is vibrated or the pressure head is loose during testing, the reading will be low.
3).Inconsistent readings
This is caused by the specimen not being firmly placed, or the indenter and load being selected incorrectly. - Summary
The Rockwell hardness test seems to be a simple test, but there are still many influencing factors. In order to obtain accurate data, all factors must be taken into consideration. The above analyzes the issues and issues that should be paid attention to during the Rockwell hardness test. As long as we pay attention to the factors that affect the results during the actual test process, I believe we can get more accurate data.