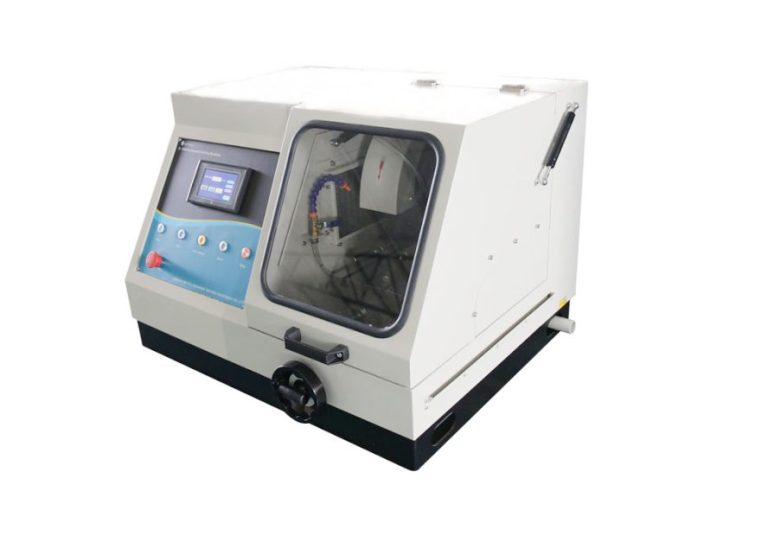
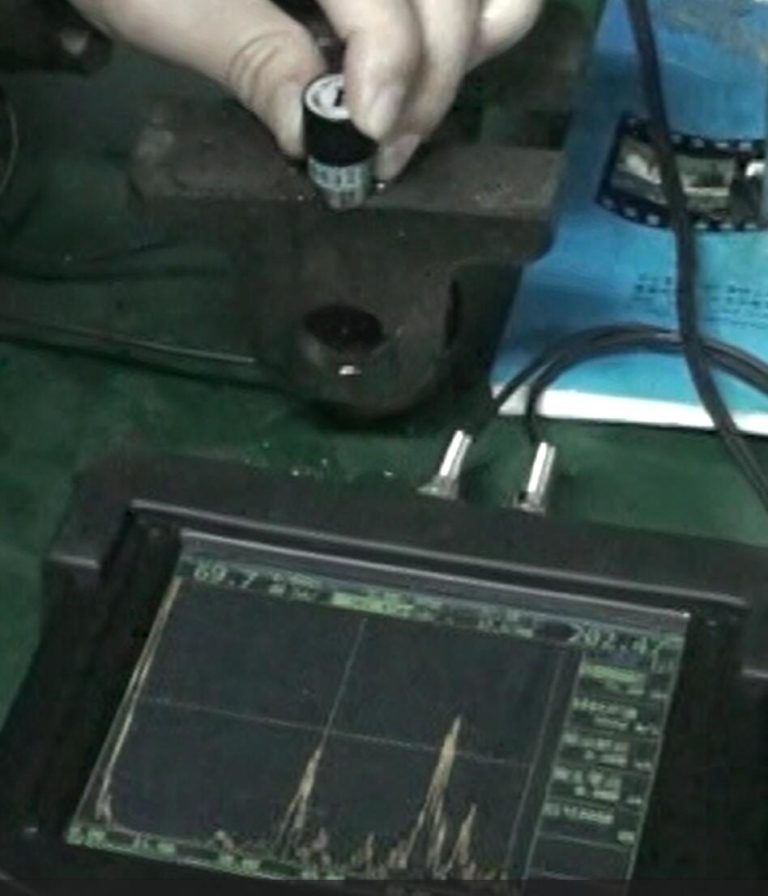
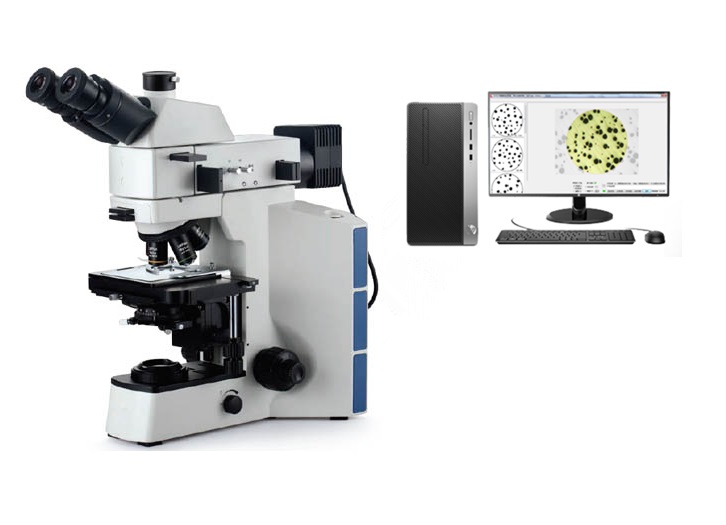
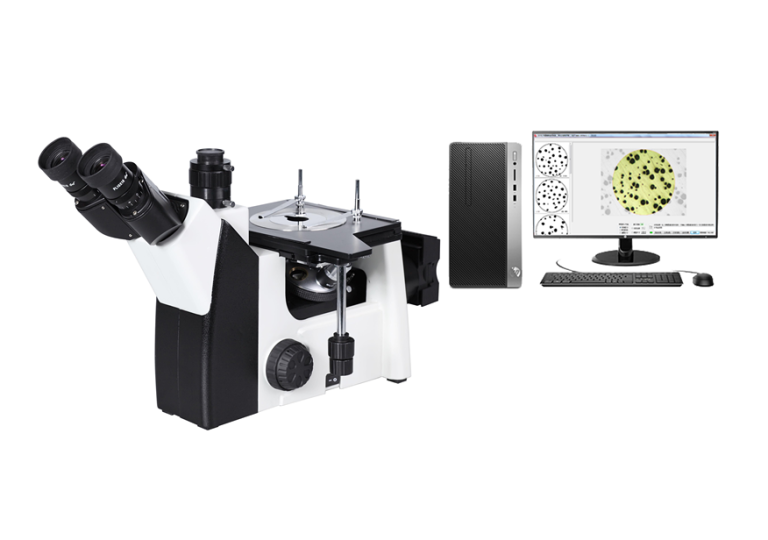
BEIJING TIME VISION AI INSTRUMENT LTD.
E-mail: timehardnesstester@gmail.com
WhatsApp: 008615201625204
——————————————————————————————————–
Eerst brachten de Verenigde Staten in 1940 de nationale norm ASA B46.1 uit. Daarna werd deze verschillende keren herzien en werd de huidige norm ANSI/ASME B46. 1-1988 “Oppervlaktestructuur, oppervlakteruwheid, oppervlaktegolving en verwerkingstextuur”. Deze standaard, het middenlijnsysteem, werd overgenomen en Ra werd als de belangrijkste parameter gebruikt; Vervolgens bracht de voormalige Sovjet-Unie in 1945 de nationale norm GOCT2789-1945 “Surface Finish, Surface Microgeometry, Grading and Representation” uit, die drie keer werd herzien en GOCT2789-1973 werd “Parameters en kenmerken van oppervlakteruwheid”. Deze norm neemt ook de middellijnsysteem en bepaalt zes evaluatieparameters, waaronder de kwadratische wortelafwijking van het profiel (Rq) en de bijbehorende parameterwaarden. Bovendien werden de meeste normen van andere industrieel ontwikkelde landen geformuleerd in de jaren vijftig uit Duitsland heeft in februari 1952 de DIN4760- en DIN4762-normen uitgegeven voor de evaluatieparameters en terminologie van de oppervlakteruwheid.
In order to study the impact of surface roughness on part performance and the need to measure surface micro-roughness, from the late 1920s to the 1930s, some experts from Germany, the United States, the United Kingdom and other countries designed and produced profile recorders and profilometers, and also Instruments that use optical methods to measure surface microscopic roughness, such as light-section microscopes and interference microscopes, have been produced, creating conditions for quantitatively evaluating surface roughness numerically. Since the 1930s, quantitative evaluation parameters of surface roughness have been studied. For example, Abbott in the United States proposed using the depth from the peak of the surface profile and the support length ratio curve to characterize surface roughness.
Published Schmaltz’s monograph on surface roughness, and made suggestions for the standardization of surface roughness evaluation parameters and values. However, the use of roughness evaluation parameters and their numerical values truly became a widely accepted standard in the 1940s when corresponding national standards were issued in various countries.
First, the United States issued the ASA B46.1 national standard in 1940. Afterwards, it was revised several times and became the current standard ANSI/ASME B46. 1-1988 “Surface Structure Surface Roughness, Surface Waviness and Processing Texture”. This standard The center line system was adopted and Ra was used as the main parameter; then the former Soviet Union released the GOCT2789-1945 “Surface Finish, Surface Microgeometry, Grading and Representation” national standard in 1945, which was revised three times and became GOCT2789-1973 ” “Surface Roughness Parameters and Characteristics”, this standard also adopts the center line system and stipulates 6 evaluation parameters including the root mean square deviation of the profile (Rq) and their corresponding parameter values. In addition, most of the standards of other industrially developed countries were formulated in the 1950s. For example, the Federal Republic of Germany issued DIN4760 and DIN4762 standards on surface roughness evaluation parameters and terminology in February 1952 .