The measurement of surface roughness is a critical aspect of quality control in various industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive. Roughness testers are instruments designed to assess the texture of a surface, providing essential data for ensuring that components meet specified tolerances and performance standards. However, the accuracy of these measurements can be influenced by several factors.
1. Calibration of the Roughness Tester
One of the primary factors influencing measurement accuracy is the calibration of the roughness tester. Regular calibration against known standards is essential to ensure that the device provides accurate readings. Calibration should be performed according to the manufacturer’s specifications and at regular intervals. Failure to calibrate the device properly can lead to significant measurement errors.
2. Surface Condition
The condition of the surface being measured plays a crucial role in the accuracy of roughness measurements. Factors such as surface contamination (e.g., dust, grease, or oil), oxidation, and wear can affect the readings. A clean and well-prepared surface is essential for obtaining reliable measurements. Additionally, the type of material and its inherent properties can also influence the results.
3. Measurement Technique
The technique used for measuring surface roughness can significantly impact accuracy. Different measurement methods, such as contact and non-contact techniques, have varying levels of precision and suitability for specific applications. Contact methods, while generally providing high accuracy, may be affected by the probe’s wear or improper contact force. Non-contact methods, on the other hand, may be influenced by environmental factors such as light interference.
4. Probe Characteristics
The characteristics of the probe used in the roughness tester, including its tip radius and material, can affect measurement accuracy. A probe with a large tip radius may average out surface features, leading to lower roughness values. Conversely, a probe that is too small may be overly sensitive to surface irregularities. Selecting the appropriate probe for the specific application is essential for achieving accurate measurements.
5. Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibrations can also impact the accuracy of roughness measurements. Fluctuations in temperature can cause thermal expansion or contraction of both the roughness tester and the workpiece, leading to measurement discrepancies. High humidity can lead to condensation on the surface, affecting readings. It is important to conduct measurements in a controlled environment to minimize these effects.
6. Operator Skill and Technique
The skill and experience of the operator using the roughness tester can greatly influence measurement accuracy. Proper handling of the instrument, understanding of the measurement process, and adherence to best practices are essential for obtaining accurate results. Operators should be trained in the correct procedures and techniques to ensure consistent and reliable measurements.
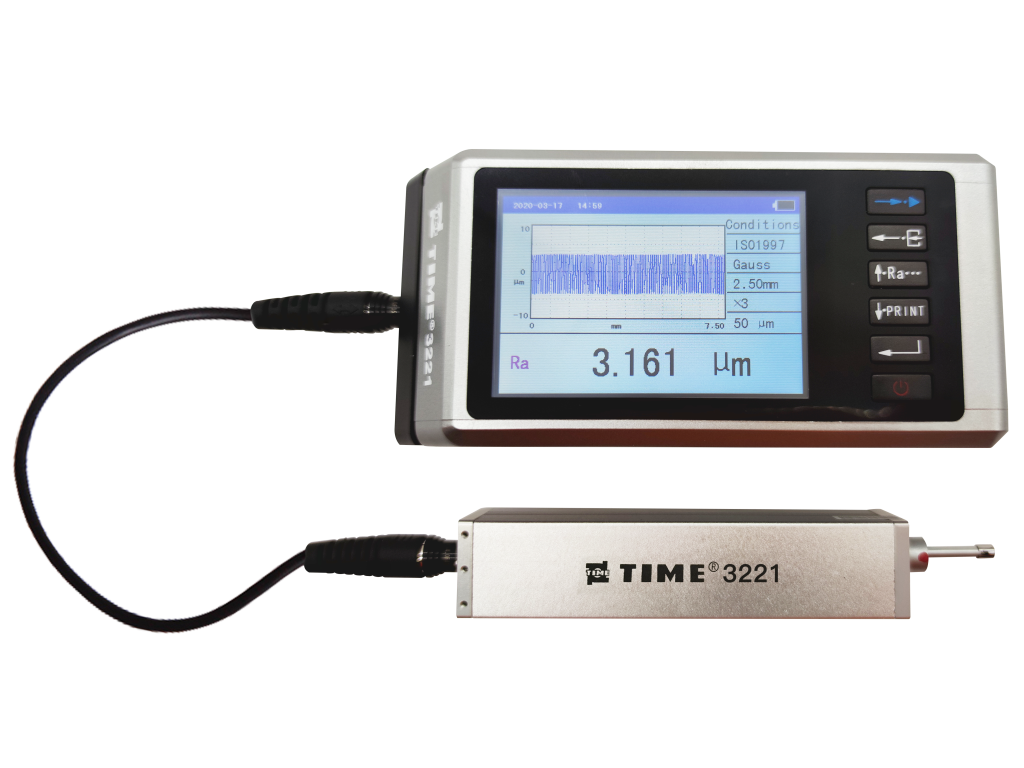
The accuracy of roughness testers is influenced by a variety of factors, including calibration, surface condition, measurement technique, probe characteristics, environmental conditions, and operator skill. By understanding and addressing these factors, manufacturers can improve the reliability of their roughness measurements, ultimately contributing to higher quality products and processes. Regular training, maintenance, and adherence to best practices are essential for achieving optimal measurement accuracy in surface roughness testing.