Conventional non-destructive testing methods include: radiographic testing, magnetic particle (or magnetic flux leakage) testing, penetrant testing, ultrasonic testing, and eddy current testing.

1 Radiographic testing (RT)
The earliest application of non-destructive testing method, it is widely used for internal defect inspection of metal and non-metal materials and products, with a history of at least 50 years. It has unparalleled unique advantages, that is, the accuracy, reliability and intuitiveness of inspecting defects, and the obtained radiographic films can be used for defect analysis and archived as quality certificates. However, this method also has the disadvantages of more complex equipment and higher cost, and attention should be paid to radiation protection.
The steel pipe inspection system is an inspection system developed and produced by our company to meet the online inspection requirements of various steel pipe manufacturers’ production lines. The detection system is seamlessly connected to the entire production line, and a secondary management system interface is reserved to adapt to the control process requirements and management process requirements of the on-site steel pipe manufacturers. Supports manual, automatic and semi-automatic detection modes. Automatic weld recognition technology facilitates automatic control in the inspection preparation stage; it has a database, and the inspection parameters of the same product can be automatically loaded with one click; dual detectors can be inspected at the same time, shortening the inspection time by half. The entire system has a high degree of automation and operational inspection. It has a high share of domestic steel pipe production lines and is the best choice for large steel pipe manufacturers.
Features
The X-ray real-time imaging detection system for straight seam steel pipes, the X-ray real-time imaging detection system for spiral steel pipes, and the X-ray real-time imaging detection system for composite steel pipes are all at the leading level in the country. It has three control modes: manual, semi-automatic and fully automatic.
Main Specifications
●Applicable pipe diameter: Φ76 ~ Φ3800mm, δ= 2~25mm(Fe), Lmax=20 m
●X-ray tube voltage: 30kV-450kV
●Industrial imaging system: digital imaging board
●Detection speed: 1-4m/min continuously adjustable
●System resolution: better than 38.5Lp/cm
●Best sensitivity of the system: 1.0-2.0%
- Magnetic particle testing (MT) or magnetic flux leakage testing (EMI)
The detection principle is based on the fact that after the ferromagnetic material is magnetized in the magnetic field, the discontinuities (defects) of the material or product generate a leakage magnetic field, which attracts the magnet powder (or detects it with a detection element) and is displayed (or displayed on the instrument). ). Therefore, this method can only be used for surface or near-surface defect inspection of ferromagnetic materials or products. - Penetration testing (PT)
Including fluorescence and coloring. Because of its simple equipment and easy operation, it is an effective method to detect surface defects that make up for the lack of magnetic particle testing. It is mainly used for surface defect inspection of non-magnetic materials.
The principle of fluorescence inspection is to immerse the inspected product into a fluorescent liquid. Due to the capillary phenomenon, the fluorescent liquid is absorbed into the defect, and the surface liquid is removed. Due to the photoinduced effect, the fluorescent liquid emits visible light under ultraviolet irradiation to reveal defects.
The principle of staining inspection is similar to that of fluorescence inspection. They do not require special equipment. They just use developer powder to suck the coloring liquid adsorbed in the defects out of the surface of the part to reveal the defects.
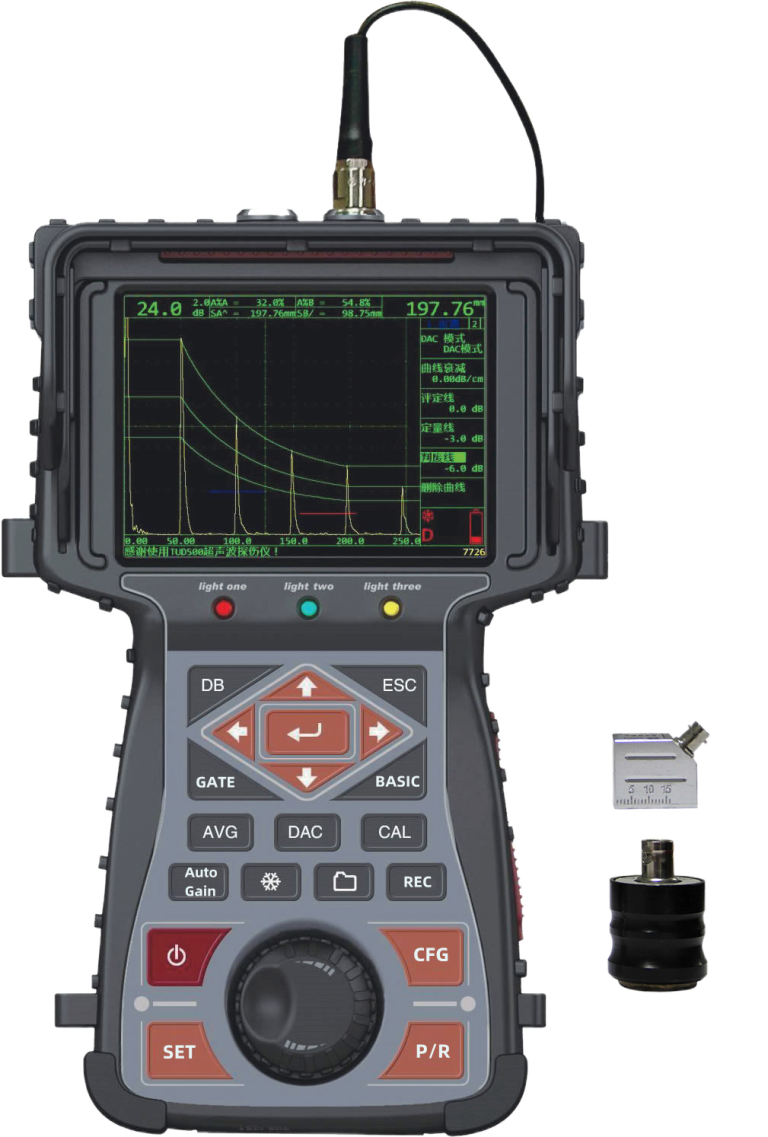
- Ultrasonic testing (UT)
This method uses ultrasonic vibration to find internal (or surface) defects in materials or parts. According to different modulation methods of ultrasonic vibration, it can be divided into continuous waves and pulsating waves; according to different vibration and propagation modes, it can be divided into four forms of longitudinal waves, transverse waves, surface waves and Lamb waves to propagate in the workpiece; according to the emission of sound waves Depending on the receiving conditions, it can be divided into single probe and multi-probe methods.
- Eddy current testing (ET)
The principle of eddy current testing is that an alternating magnetic field generates eddy currents of the same frequency in the metal material. The change in the relationship between the size of this eddy current and the specific resistance of the metal material is used to detect defects. When there is a defect on the surface of a metal material (such as a crack), the specific resistance there increases due to the presence of the defect, and the eddy current associated with it decreases accordingly. The small changes in eddy current are amplified and indicated by an instrument. , the existence and size of defects can be revealed.